University of Washington Wireless Networks Reference (2022-03-29)¶
Overview¶
The University of Washington offers three wireless SSIDs to support the networking needs of students, staff, and faculty. These networks serve slightly different purposes with each one employing a distinct security configuration to ensure that Internet access is restricted to current students, staff, and faculty.
The University of Washington SSID is an open network that employs a captive portal. In order to access any site outside of the UW network, you must authenticate your session using your NetID username and password. Since a browser is needed at the time you connect, this is not an ideal solution for a headless network device.
The eduroam SSID is an encrypted, WPA2 Enterprise network that requires new device onboarding before making a connection.
The UW MPSK network is an encrypted WPA2 Personal network, much like the one you might use at home, except that an online onboarding step (described in the next section) is required for each device you want to connect.
Additional information about these networks is available at https://itconnect.uw.edu/connect/uw-networks/campus-wi-fi/.
UW MPSK Network Onboarding¶
The UW MPSK network is a good fit for gaming consoles and IoT devices that operate without a screen and keyboard. To connect to his network, you will need to register through the UW IT website and obtain a passphrase (which is unique to each device).
In order to complete these instructions, you will need the following information:
- Your NetID and Password
- The MAC address of the device you want to register1
http://register.wifi.uw.edu/guest/mac_create.php
Eduroam Onboarding¶
In prior years, access to eduroam relied on username/password authentication through the University's NetID system. Authentication was performed by the wireless client -- wpa_supplicant in our case -- when connecting to the system. If a user had a valid NetID, no prior registration was needed.
As of February 2022, the university quit accepting NetID based connections and began requiring all wireless clients to be registered and set up ahead of time with a client certificate. UW provides a portal and tools that automate most of this process for mainstream desktop systems; however, those tools aren't compatible Raspberry Pi OS.
The following instructions will guide you through connecting to the onboarding portal, registering your device, downloading your client identity certificates, and installing these credentials onto your Raspberry Pi. In order to complete these instructions, you will need to gather the following information:
- Your NetID and Password
- The MAC address of the device you want to register1
- A passphrase that will be used to encrypt your new certificates.
Register and Download Identity Certificates¶
From your workstation, open a browser and navigate to http://onboard.wifi.uw.edu/. You will be directed to a page that instructs you to Click to configure eduroam and identifies your current device.
Do not click on the Sign In button immediately. Before you do so, you will need to select an alternate device type at the bottom of this screen. Select User-Defined from this drop-down list and then proceed to Sign In to be directed to the UW single sign on page.
After successfully logging in, you will be presented with a form that can be used to generate a new certificate. Fill out the requested details, entering a description of the device you’re connecting, such as "Raspberry Pi" or "INFO314 Pi", and then carefully typing or pasting your MAC address into the field labeled MAC Address.
After you press the “Create” button, you will be prompted to enter a passphrase. The text you enter here will be used to encrypt your new certificate and its private key. You will need to use this passphrase again later.
On the following screen, click on the link labeled P12 to download a file containing your certificate and private key. Take note of the P12 filename before proceeding.
On the final screen, record a copy of the settings displayed in the section that says Please use the following settings to configure your device. You will need these values to complete the wpa_supplicant network configuration.
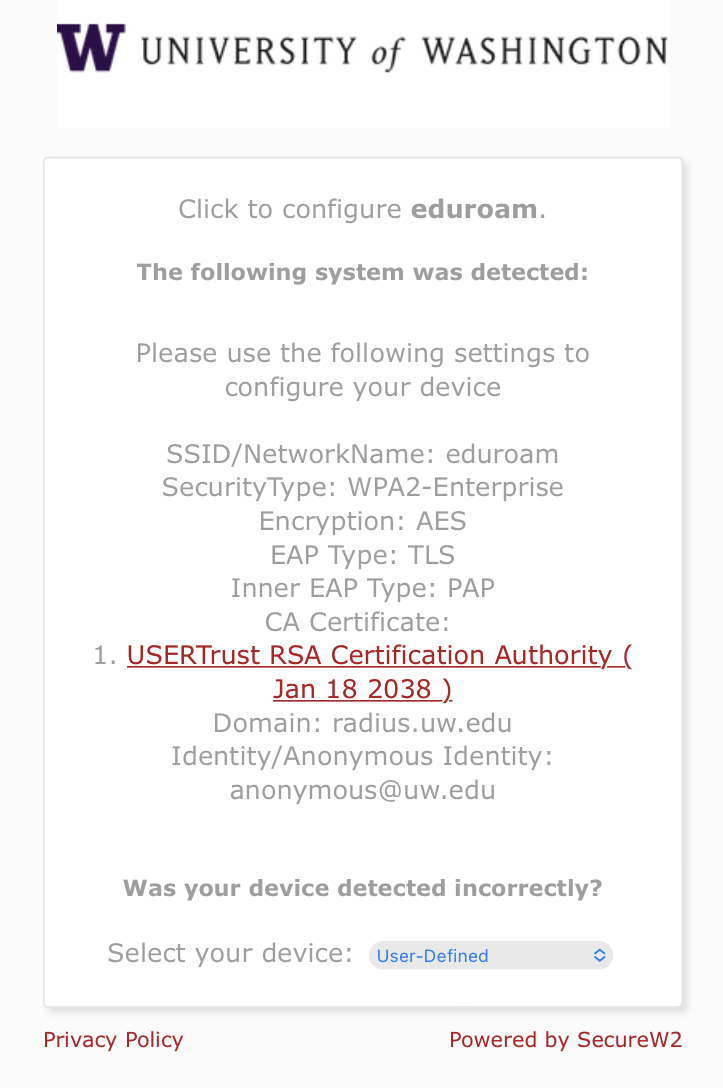 .
.
Before you leave this page, click on the link for the CA Certificate in order to download a copy of to your computer.2 Take note of this filename as well.
Install certificates to your device¶
Before configuring wpa_supplicant, we will need to convert the files downloaded during onboarding into a format supported by the software, and install them into an appropriate location. The client certificate and private key (credentials that are used to identify you to the network) are stored in a passphrase encrypted PKCS#12 file. This is the first file that you downloaded from the P12 link.
Copy the files you downloaded in the previous step into the home directory of your Pi. Extract the client certificate and the private key into separate PEM files using the openssl command-line utility.3 4
# Extract the client certificate and convert to PEM
openssl pkcs12 -in "<P12_FILENAME>" -out <NETID>_cert.pem -clcerts -nokeys
# Extract the private key and convert to PEM
openssl pkcs12 -in "<P12_FILENAME>" -out <NETID>_key.pem -nodes
You should now have two new pem files in your home directory. Move these files along with certificate authority into /etc/wpa_supplicant/ and make a note of their names.
Info
No conversion is necessary for the certificate authority. The file that you downloaded is already in the PEM format.
Before you wrap up, update the ownership and permissions of the certificate files to further protect them. This is particularly important for <NETID>_key.pem, which now contains an unencrypted copy of your certificate's private key.
Cleanup¶
Retain a copy of the certificates and configuration information in case you need to repeat this process later. You will also need the passphrase in order to decrypt the p12 file. Store this value in a safe place.
For now, you may leave the downloads in the home directory of your pi so that they are available if you need to troubleshoot this process. Once your connection to the eduroam network is verified, you can safely remove both files.
-
You can look up MAC addresses on your pi using the
ip linkcommand. Your device will display a different MAC address (labeledlink/ether) for each network interface. Register the address associated with the wireless interface --wlan0by default. ↩↩ -
The Certificate Authority (CA) certificate is a public credential that your device uses to verify that you are speaking to a legitimate server. ↩
-
All caps text enclosed in angle brackets are placeholders. Fill in these values before running the code. ↩
-
You will be prompted for your passphrase in order to convert the file. ↩